- One of the most important features that distinguish people from each other is their hair.
- Hair has been accepted as an indicator of factors such as health and youth.
- We try to complete our appearance by shaping our hair color, shape and length according to our tastes and tastes.
What is the hair ?
- Hair is the general name given to the hair cluster on the head in humans.
- Hair grows faster than other hair clusters. The average hair growth rate is 0.3 mm to 0.4 mm per day.
- Since the growth and pause phases of each hair are independent of each other, while one hair grows, the other hair may fall out.
- The average hair thickness of a man is 0.03-0.04 mm.
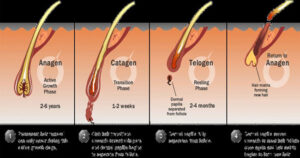
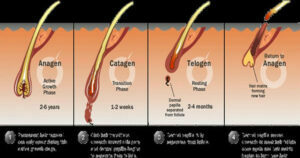
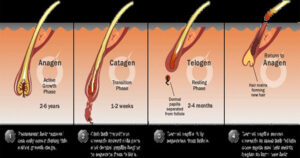
Hair Cycle
- In the natural life cycle of the hair, the hair grows for a certain period of time. In the next stage, elongation stops and shedding begins.
- The hair follicle is restructured after the shedding and after this resting period, it starts to grow again by renewing itself from where it was.
- Anagen phase: It is the healthy growth phase of hair. About 80-90% of hair is in the anagen phase. This phase can last up to five years, with an average of three years for each hair strand.
- Catagen phase: It is a transitional period that lasts about three weeks. During this period, hair thinning and loss of pigment begins. About 2 percent of our hair is in the catagen phase.
- Telogen phase: It lasts an average of three months. Hair that has thinned and lost pigment begins to fall out. In the same period, a new follicle begins to form from the hair cells. About 10-15 percent of hair is in the telogen phase.
- In newborn babies, all hairs are in the same circuit. For this reason, 2-3 week old babies suddenly experience hair loss. After 6 months, the hair fits into the hair pattern of adults.
Hair Colors
- The pigments that give color to the hair are yellow, red and blue. Yellow pigments have the smallest volume and blues have the largest volume. Blue pigments are the outermost, red is the middle and yellow is the innermost.
- For this reason, while the hair color is lightened by chemical means, the hair first loses its blue color and turns red, and finally becomes yellow. If the process is continued, a white or very close to white tone can be obtained.
- The absence of pigments in the body causes the condition called albino. In albinos, usually all hairs are colorless.
Blondes Have More Hair

- Hair color also determines its density. A normal person has 100,000 hair follicles. Each of these hair follicles has the capacity to produce 20 hairs throughout a human life. The number of hair follicles in blondes is around 146 thousand. In other words, there is more hair production. The number of roots in red hair is 86 thousand.
Bleaking Hair
- While starvation occurs, the melanocyte injects pigment (melanin) into the keratin-containing cells. Keratin is the protein that makes up our hair, skin and nails. Over the years, the melanocyte continues to inject pigment into the keratin in the hair, and thus color is formed.
- As age progresses, melanin begins to decrease. The hair turns gray and eventually turns white.
So why does our hair turn gray or white?
- Professor of cell biology at the University of Bradford in England, Dr. Desmond Tobin thinks that the hair follicle has a ‘melanogentic clock’ and this event reduces the pigment in the hair by slowing or stopping melanocyte activity.
- The roots always look pale as this happens while the hair is getting ready to shed.
- Also, Dr. Tobin says that hair can also turn gray due to age and genetic factors.
- Because genes can calculate the end of the pigment potential of each hair follicle. This happens to different degrees in different hair follicles. In some people this is a fast-growing condition, in others it happens slowly over several years.
- In a February 2005 science article, Harvard scientists wrote that failure of melanocyte stem cells to continue producing melanocytes can cause graying of hair. This defect in the protection of melanocyte stem cells can lead to the deterioration of the marks that give the hair its color.
- There are other factors that can alter the hair pigmentation. Thus, the hair can take on a lighter or darker color. Scientists have divided these into intrinsic (internal) and extrinsic (external) factors: Internal factors can be shown as genetic defects, hormones, body distribution and age. External factors are climate, pollution, exposure to toxins and chemicals.
Hair Loss
- Hair falls out for many reasons. An accurate treatment approach cannot be provided without determining the cause of the spill. Therefore, it is important to know the reason for the shedding.
- Male patHair loss can be seen in both men and women. Hair loss, which is more common in men, affects 25 % of men until the age of 25, 40 % by the age of 40, and 50 % by the age of 50.
- tern hair loss can be on both sides of the forehead and on the top, as well as completely covering the entire head. In women, shedding is mostly manifested in the form of thinning of the hair.
- Before starting a treatment, the type of hair loss should be examined by a specialist doctor. Many diseases, hormonal and metabolic disorders and nutritional effects can trigger hair loss. Treatment is never complete until such causes are eliminated.
- We should pay attention to the cosmetics we use to prevent hair loss. Using natural olive oil, almond oil, laurel oil, shampoo and soaps for hair cleaning helps prevent hair diseases, dandruff and hair loss. Health products available in pharmacies should be preferred instead of chemical shampoos.
- MALE TYPE (ANDROGENIC ALOPE) HAIR LOSS
- FEMALE TYPE HAIR LOSS 95 % ANDROGENIC
- Alopecia

- The first medical description of androgenetic alopecia was given in BC. It is said that Aristotle made it in the 4th century. The philosopher described the relationship between baldness and sexuality.
- Research on baldness was also seen in the Ottoman period and in Egypt. Years later, some studies worked in this direction again, they determined that the men who were sterilized did not go bald, and they conducted research during the reign of Abdülhamit.
Androgenic Alope
- The main cause of genetically based hair loss is thought to be the 5-Alpha Reductase enzyme, which converts the male hormone testosterone to dihydrotestosterone. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) shows its effect by binding to androgen receptors on hair follicles. DHT causes shortening of life cycles of hair follicles. With each repetition of the cycle, the hair becomes a little weaker, and as the process is repeated, the scalp becomes visible.
- Although everyone has the hormones and enzymes that cause hair loss, why do some people lose their hair and some don’t?
- The answer to this question can be explained by a few theories based on observations made in recent years, especially in hair surgery.
- It is known that hair growth is determined before birth. The cause of hair loss is the inherited sensitivity of hair follicles to DHT.
- The higher the ratio of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) to testosterone,
- The faster the hair loss process will develop. As it is understood from this, male pattern hair loss is not related to the amount of male hormone, but to what level of DHT is produced.
- The number of androgen receptors on the scalp of patients with male pattern hair loss is above the normal value.
- Hair that sheds in a certain pattern as male pattern baldness or female pattern baldness shows hereditary characteristics and the person has genes that reveal hair loss.
- In men, the hair loss gene can be inherited from a single person by the mother or father, and if both parents have hair loss, the risk of hair loss is very high.
- In women, hair loss in only one of the parents is ineffective in creating hair loss due to the high level of estrogen hormone in women. There are many other causes of hair loss, they should not be confused with genetics.
- normal hair loss
- Hair that has reached the end of its life is shed by itself or by external effects (such as combing, washing with shampoo, brushing, shaping the hair). Instead, new hair grows. An average of 100 or sometimes 200 hairs are shed per day. Hair loss seen in newborn babies and pregnancy can be considered as partly normal hair loss.

- Hair loss due to stress
- The relationship between skin diseases, stress and mental events has been known for a long time. The person may reflect his/her psychological problems as a dermatological problem. In addition, a spontaneous skin problem (hair loss) can lead to individual, psychological disorders and even psychosocial negativities that will damage the body image of the person. Briefly, there are two kinds of relationship between hair loss and stress:
- The first relationship is supported by a neurotic mental structure, and hair loss, fueled by stress, may occur without an apparent organic cause.
- The second relationship is the psychological reactions that the person develops against the appearance resulting from hair loss.
Hair Loss In Women
- The lifeless appearance of the hair, thinning of the hair strands and hair loss problems are the problems that one out of every three women complain about in some part of their life.
- Genetic Type Hair Loss
- An important part of women’s hair loss problems is genetic type hair loss.
- The psychological effect of male pattern hair loss, which is seen in 30 million women in the USA, is more severe in women than in men, and it is experienced as a more severe stress. While men consider male pattern hair loss acceptable, this is not the case for women.
- The incidence of male pattern hair loss in women is 70%.
- Before diagnosing male pattern hair loss in women presenting with hair loss, it should be investigated whether there is any underlying disease. For example, factors such as hormonal, systemic diseases, cancer, unbalanced nutrition, infection, drugs, chemical agents should be questioned. If a woman has male pattern hair loss, hair transplantation can be applied.
- 20%* of women with female pattern hair loss have a family history.
- Hair loss starts at a late age and progresses slowly. Regular hair loss occurs and shedding usually peaks at the age of 40. Shedding seen at an early age is more serious.
- Genetic type of hair loss is observed differently in men and women; In men, it generally starts from the temples and progresses to the top, while in women it appears as weakening and thinning of the hair in general.
- This shedding typically starts in the middle area of the hair and usually progresses by preserving the anterior hairline and temporal region. For a correct diagnosis, family history should be examined and inquiries should be made about previous diseases and medications used. Since female pattern hair loss thins all hair follicles, it is not considered a suitable candidate for hair transplantation.
- Hormone Imbalances
- Apart from genetic hair loss, another important cause of hair thinning and loss in women is hormone imbalances and hormone treatments. It is observed that the birth control pills used often cause hair loss.
- Thyroid Disease and Iron Deficiency
- Hair loss is also seen during the treatment of hormone disorder related to the over- or under-functioning of the thyroid gland, which is known as hyper and hypothyroidism in medicine.
- Iron deficiency anemia can be caused by heavy menstrual bleeding or not consuming too much iron-rich foods. Iron deficiency is one of the most important causes of weak-looking hair and hair loss in women.
- Unbalanced Nutrition and Stress
- Malnutrition is also one of the factors that cause hair loss. Especially in unconscious diets and one-way nutrition, the hair cannot get enough vitamins, minerals and protein, which is the building block of keratin in its structure, which are necessary in its life cycle.
Hair Loss Treatment In Women
- A different diagnostic scheme is used in women who have lost their hair than in men. Three important building blocks in women’s hair health should be analyzed in detail. These;
- Hormones
- Diet and other drugs used
- It can be summarized as genetic reasons.
- The diameter of the hair strand and the hair density are measured and recorded at the first visit of the patient. The quality of hair root units is marked. In the systemic blood analysis, THYROID, URINARY AND OVARIAL HORMONES table is created. If there are remarkable deviations in this table, the relevant physicians are referred.
Hair Treatments
- The starting point of the spill is recorded. According to the stage and the result of the examination, the HAIR SUPPORTS that women benefit most are as follows;
- Regulation of hormones
- Regulation of diet and vitamin enzyme supplements
- PRP
- Hair mesotherapy
- Topical hormones
- Home use training of topical hair remedies
- Natural nutritional supplements- natural hair cures
- Washing the hair with the right water-shampoo
Hair Mesotherapy
- “Hair Mesotherapy”, which is among the most effective and important local methods in hair loss, is the application of vitamins, antioxidants and drugs that increase blood circulation to the hair follicles with the help of fine-tipped needles.
- Since the hair follicle is located in the dermis layer of the skin, the effect of externally applied drugs on the scalp is limited. With mesotherapy, the effect is achieved in a short time as the substances missing from the hair follicle are given directly to the hair root in small doses.
- Hair Mesotherapy can be applied locally, it acts to stop hair loss, increase the quality of existing hair and activate hair growth by stimulating cell metabolism in the desired area. In addition to preventing shedding, it makes the hair look more lively, shiny and voluminous.
- Hair loss due to stress, seasonal and metabolic disorders and sudden hair loss after pregnancy benefit from mesotherapy. It is beneficial to apply mesotherapy especially in the “initial phase of androgenetic alopecia”, where a shrinkage is observed in the hair root and shortening is detected in the “anagen phase”, which is the formation and growth phase of the hair. In hormonal and genetic hair loss, this method can be preferred as a supportive treatment.
- The content of the mixture used in the mesotherapy application can be arranged according to the needs of the person. The substances that make up the mixture content; blood circulation-enhancing vasodilators, connective tissue regeneration agents, vitamin B5 and biotin.
Hair Treatments

- HAIR TRANSPLANT
- BIOFIBER HAIR TRANSPLANT
- HAIR CLONING (FUTURE…)
Biofiber Hair Transplant
- It is a crude form of hair transplantation; but instead of your own donor hair, synthetic fibers are implanted in your head. These transplants use NIDO, a man-made polymer. These nylons are planted directly on your scalp in small batches.
- Although this method is not used in the USA, it is widely practiced in Japan and other countries, many US doctors have treated men who experienced the disastrous results of these implants made in another country.
- The fibers are shiny, artificial-looking and hard. The texture of the fibers does not look like hair and does not feel like hair. These implants cause chronic infections in the area where they are made, and over time, the swelling and infections can destroy the scalp.
- At the bottom of these fibers, plugs (sebum) formed from the natural oils of the scalp form, and these plugs must be removed every few weeks and the ongoing infection should be taken care of.
Hair Folclue
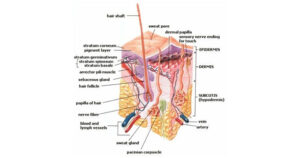
Hair follicle:
- Hair
- Volume
- Muscle
- Root sheath
- Sebaceous gland
The follicle is the structure in which the hair grows. The porous structure of the hair produces oil and lubricates the skin and hair. There are special muscles in the parts that can be seen outside the porous structure.
Follicular Unit
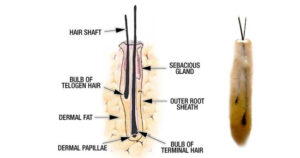
- What is a follicular unit? The follicular unit is the natural hair bundle formed by more than one hair follicle. These units can be distinguished under a three-dimensional microscope.
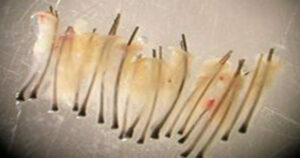
First Hair Transplant
- A dermatologist named Dr. Norman Orentreich performed the first hair transplant in 1959. In the first hair transplantation, the roots of the hairs, which are technically difficult to shed behind the nape, were transplanted to the hair roots that started to become sparse or shed. The durable roots on the back of the neck are called “donor dominance” in the medical language.
- Unfortunately, these operations did not give the desired
- result due to the transplantation of large grafts.
Fue
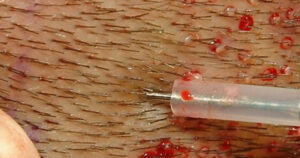
- FUE “Folicular Unite Extraction” is the abbreviation of the term. The roots to be transplanted are obtained by removing the follicular units one by one with a special tool.
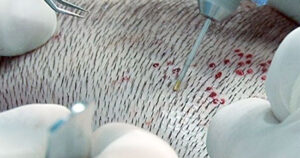
- This method, as a technical principle, allows the hair on the body to be removed and used.
- The advantage of the method is that the locations of the roots removed one by one are not clear, that is, there is no trace.
Micromotor

- 1MM PUNCH : 8.20 GRAFT cm2
- 0.75MM PUNCH : 20 GRAFT cm2
Effective Graft Concept

- 0.8 MM PUNCH İLE X 2500 GRAFT : 1.8 X 2500: 4500 HAIR
- 1 MM PUNCH İLE X 2000 GRAFT : 2.5 X 2000: 5000 HAIR
DONOR AREA

- HAIR AND BODY HAIR
- NECK, NECK, BEARD, TOP OF CHEACH
- CHEST, SHOULDER, BACK, LEG
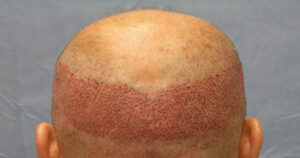
- Genetic androgen sensitivity affects certain areas of the head.
- The hair circle between the two ears is defined as “permanent hair”, these hair follicles do not have a genetic sensitivity to DHT and continue their existence throughout life.
With Fue, The Donar Remanson The Field
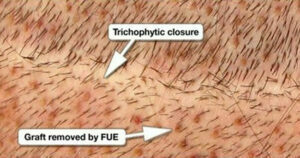
Chest Hairs
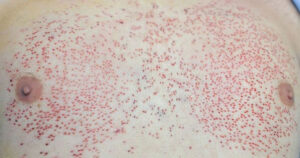
Beard Region Donorfield
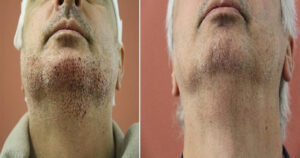
How To Detemine The Frequency Or Hair Transplant
- Scientific researches show that the density of 80 medium hairs per square centimeter can completely cover the skin.
- However, this frequency is related to the person’s Follicular Units being rich or poor in hair follicles.
- While “Units with more triple roots” provide a sufficient frequency of 30 units per square centimeter, this number rises to 40 in “more binary Units”.
Hair Frequency
- Normally, a hair consists of 70 to 100 follicular units per square centimeter (FU/cm2).
- According to the results obtained in scientific studies, hair loss becomes noticeable when hair density decreases by 50 percent.
- This can also be called “felt density”, which manifests differently from mathematical density. The density felt is a hairy appearance starting from 50 follicular units per square centimeter.
- It is the frequency in which less than 20 follicular units per centimeter are diluted, and less than 10 units are shed and the skin is completely selected.
- According to this result, 50 follicular units per square centimeter would be sufficient for a hair transplant.
- This is why some people achieve a natural and intense result with less than 30 follicular units per square centimeter, while others require more than 65 follicular units per square centimeter to reach a natural density.
- For a natural-looking result, it is very important how and with which instruments the channels where the follicular units will be placed are opened.
Natural Front Hairline
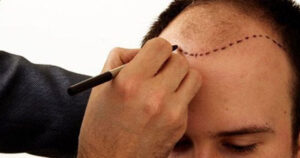
Sucess In Hair Transplant
- What are the important criteria for getting the best results from hair transplant?
- Obtaining a Natural Looking Hairline: The hairline should be in harmony with the relevant borders on the face and therefore should be evaluated within certain mathematical rules in terms of aesthetics.
- Placement of Follicular Units: Follicular units help to forget hair loss by providing the desired naturalness and visual fullness.

- Size and Depth of Micro-Incision Defining the Canal: The incision should be as small as possible on the one hand, and large enough to match the size of the follicular unit on the other. Thus, after hair transplantation, the adaptation of the roots to the recipient points is facilitated and the interruption of blood circulation in the recipient area is kept at a minimum.
- The Angle and Direction of Each Incision Must Be Precisely Defined: Micro-incisions are placed on the skin in the direction of the original hair, as they will determine the direction in which the transplanted hair will grow in the future. Thus, after the hair transplant, the hair grows in the right direction.
Hair Channels
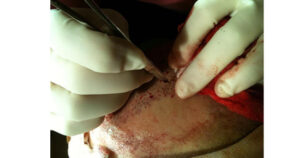
- In the area to be planted, channels are opened with special blades we call slit, and sowing is performed with a microscope and again using microsurgical instruments. Opening the hair channels is one of the most important steps for a natural result. In addition, opening channels with slits offers the advantage of not leaving any traces on the planted roots.
After Hairtransplant
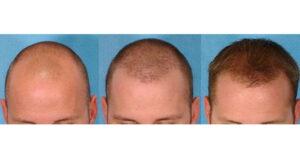
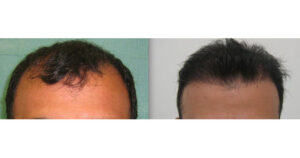
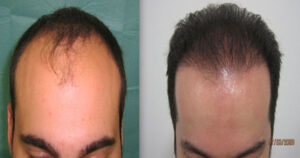
- It is inevitable that the transplanted hair will fall out in the first 3 weeks. It is not hair follicles that shed, but strands of hair. In the weeks following the shedding, healthy hair strands that will never shed again will emerge from the new roots, and within a period of 3 to 6 months, these will gradually become longer and thicker, and the appearance will gradually improve. In the 6th month, the hair grows impressively.
- However, it takes its best form within 1 year after completing the adaptation process of the transplanted hair. Since the hair belongs to the person, it comes out in the same color and character. In hair transplantation, the amount of hair and the way it is taken are as important as the direction of the transplanted hair, the naturalness of the front hairline is at least as important as the amount of transplanted hair.